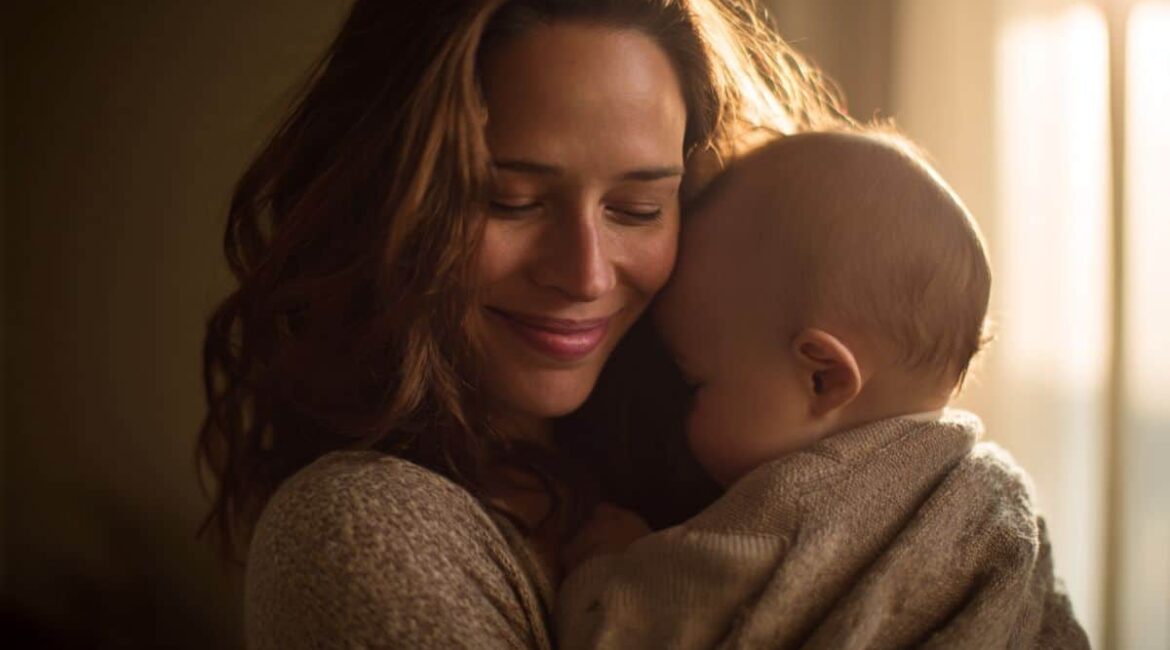
Summary: A new study shows that oxytocin nasal spray helps mothers with postpartum depression interact more positively with their babies. After receiving oxytocin, mothers expressed more warmth, affection, and physical contact, reporting a greater sense of positivity during playtime.However, the spray did not improve caregiving sensitivity or reduce stress levels,...
Popular Pain Medication Has a Mental Decline Danger.
Summary: A large U.S. medical records study has found that adults prescribed gabapentin six or more times for chronic low back pain face significantly higher risks of dementia (29%) and mild cognitive impairment (85%) within 10 years. The risks were especially pronounced in younger adults aged 35–64, where rates of...
How Your Mental Transforms 2D Into 3D in reverse images
Summary: Researchers have uncovered how primate brains transform flat, 2D visual inputs into rich, 3D mental representations of objects. This process, dubbed “inverse graphics,” works by reversing the principles of computer graphics — starting from a 2D view, through an intermediate stage, to a 3D model.Using a neural network called...
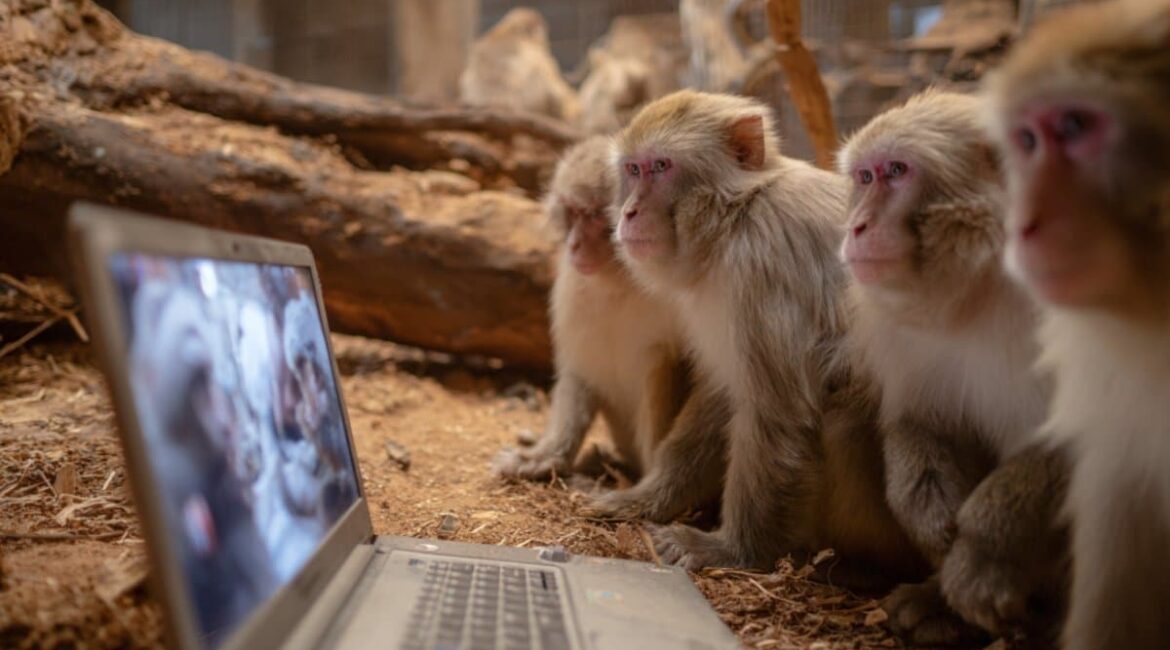
What Monkeys Like to See Most: Common Eyes and Fightings
Summary: A new study reveals that long-tailed macaques, like humans, are most captivated by videos featuring social conflict and familiar group members. Researchers showed the macaques videos of monkeys engaged in fighting, grooming, running, or sitting, and found they spent the most time watching aggressive encounters.They also preferred watching members...
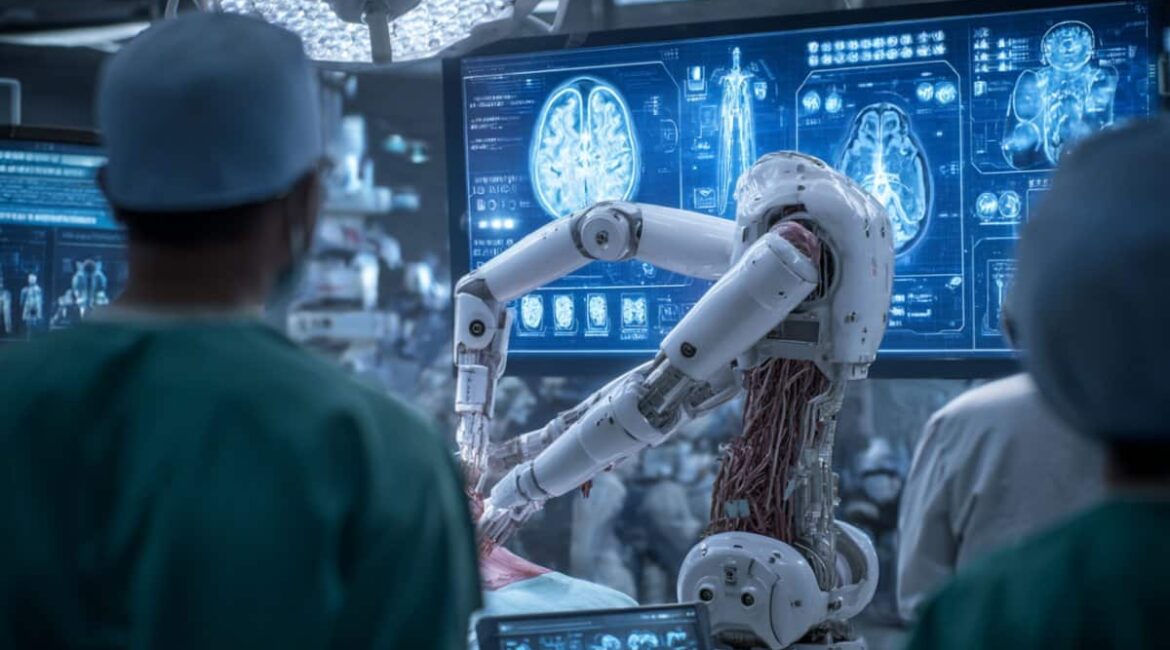
Robot Completes Complex Surgery freely with the aid of AI coaching.
Summary: A surgical robot trained on real procedure videos performed a critical phase of gallbladder removal autonomously, adapting to unexpected situations and responding to voice commands. This breakthrough shows how artificial intelligence can combine precision with the flexibility needed for real-world medicine.The robot, using a machine-learning framework similar to ChatGPT,...
Mental and Eye Barriers Found to Be Wrinkened by Cancer Pathway
Summary: Researchers have uncovered a surprising connection between a cancer-related signaling pathway and the blood-brain and blood-retina barriers. The study shows that the tumor-suppressing protein p53 weakens the Norrin/Frizzled4 pathway, which is crucial for maintaining these protective barriers.This suggests that cancer therapies boosting p53 might unintentionally compromise brain and eye...
Memory Picks Meaning Rather Than Surface Similarities
Summary: Memory helps us make sense of the present by retrieving past experiences based on either surface-level similarities or deeper conceptual connections. A new study reveals that when a familiar mental category — like excuses or conflicts — is available, memory prioritizes structural, abstract links over superficial cues.This insight clarifies...
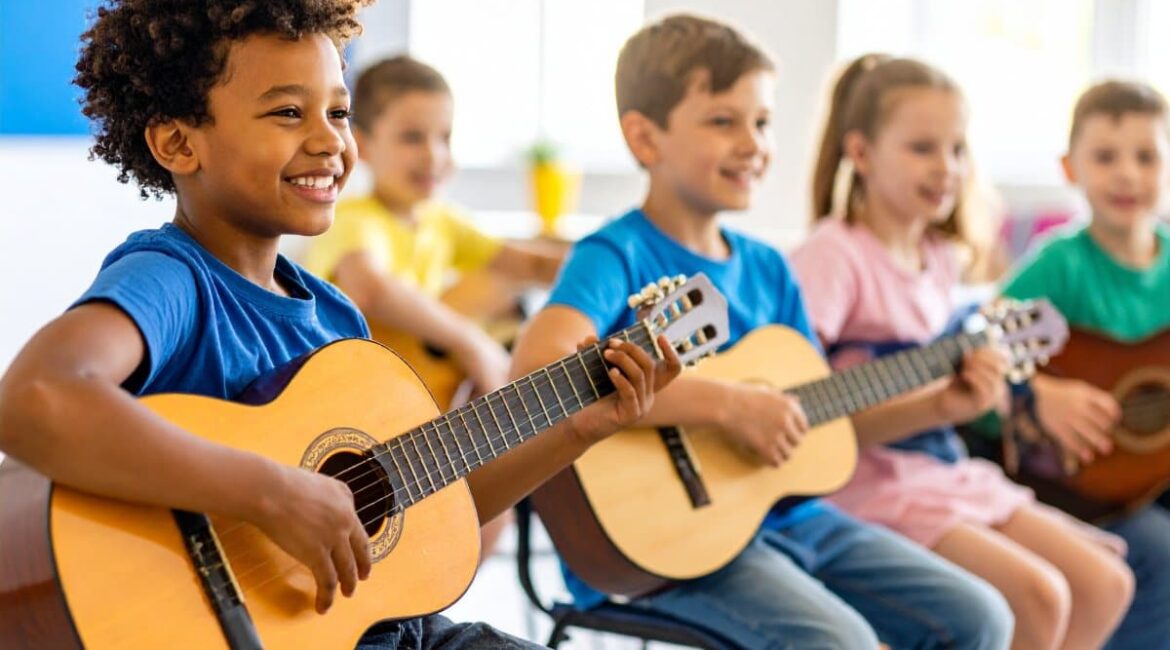
Learning audio promotes children’s well-being, self-assurance, and belonging
Summary: A new study highlights the powerful role of music learning in improving children’s social, emotional, and educational wellbeing. Beyond listening or casual participation, learning music builds self-confidence, emotional awareness, and a sense of belonging.Researchers argue music education should be seen as an essential wellbeing strategy in schools, not just...
Dopamine behaves directly, but not globally.
Summary: New research has overturned decades of belief about how dopamine communicates in the brain, showing it acts with pinpoint precision rather than broad diffusion. Scientists discovered that dopamine is released in localized hotspots, allowing highly specific and timely messages to nerve cell branches.This dual signaling system enables dopamine to...
Lab-Grown Neurons Experiment With New Diversity
Summary: Researchers have created over 400 distinct types of human nerve cells in vitro, vastly expanding the diversity available for neuroscience research. By systematically combining genetic engineering with morphogen signaling molecules, they mimicked the intricate variety of neurons found in the brain.This breakthrough opens the door for more precise disease...