Summary: A new study tested how humans and ChatGPT understand color metaphors, revealing key differences between lived experience and language-based AI. Surprisingly, colorblind and color-seeing humans showed similar comprehension, suggesting vision isn’t essential for interpreting metaphors.Painters, however, outperformed others on novel metaphors, indicating that hands-on color experience deepens understanding. ChatGPT...
In 30 Days, Mindfulness Meditation Increases Interest Across All Ages
Summary: A new study shows that just 30 days of daily mindfulness meditation significantly improves attentional control, regardless of age. Using precise eye-tracking methods, researchers found that mindfulness enhanced reaction speed, focus, and resistance to distractions.These cognitive benefits were seen in young, middle-aged, and older adults alike, highlighting mindfulness as...
Real or perception? Reevaluating our perceptions of reality
Summary: A new study challenges the notion that society is as polarized as many believe, revealing that perceptions of division often stem from the consensus within one’s own social circles. Researchers developed a novel method to distinguish actual opinion divergence from how polarized people feel society is.The findings show that...
Health: Harmonizing Modern Life With Biological Clocks Is Undermined By Artificial Lighting
Summary: New research reveals that artificial light at night disrupts more than sleep, affecting immune function, metabolism, mood, and brain health. Circadian rhythms, finely tuned over millions of years, regulate critical biological processes and can be thrown off by modern lighting and irregular schedules.Clinical trials are now exploring how light-based...
Hidden Stars of Brain Rhythms Revealed: Invisible Actors of Blood Patterns Take the Lead
Summary: New research highlights how astrocytes, long considered mere support cells, actively shape brain network dynamics. Using computational models and machine learning, researchers showed astrocytes fine-tune synchronized neural activity crucial for memory, attention, and sleep.These glial cells subtly influence rhythmic brain states, undetectable by conventional metrics but revealed through advanced...
The extent of exercise’s benefits for mental health depend on perspective.
Summary: A new study reveals that the mental health benefits of exercise depend not just on the amount of physical activity, but also on the context in which it occurs. Researchers found that leisure-time activities like yoga or team sports tend to improve mood more than obligatory tasks like housework.Factors...
Later-Born cells mature faster to maintain network stability
Summary: The brain depends on a delicate balance between excitatory and inhibitory neurons to function properly. A new study reveals that inhibitory neurons born later in development mature more quickly than earlier ones, allowing them to catch up and integrate evenly into neural networks.This accelerated maturation is controlled by genetic...
Find Exercise You Enjoy: Personality Shapes Fitness Success
Summary: A new study shows matching your personality to the type of exercise you enjoy may help you stick with it and reduce stress. Researchers found extroverts preferred high-intensity workouts, while people high in neuroticism favored short bursts of activity and saw greater stress reduction from exercise.Conscientious individuals were generally...
With Special Neurological Tabs, The Mind Transfuses Time Into Memories
Summary: Our brain doesn’t just record time—it organizes our lives into distinct, memorable moments. New research reveals that neurons in the lateral entorhinal cortex generate unique “jumps” in activity when something meaningful happens, creating bookmarks that structure our experiences.These jumps separate the continuous flow of sensations into individual events, making...
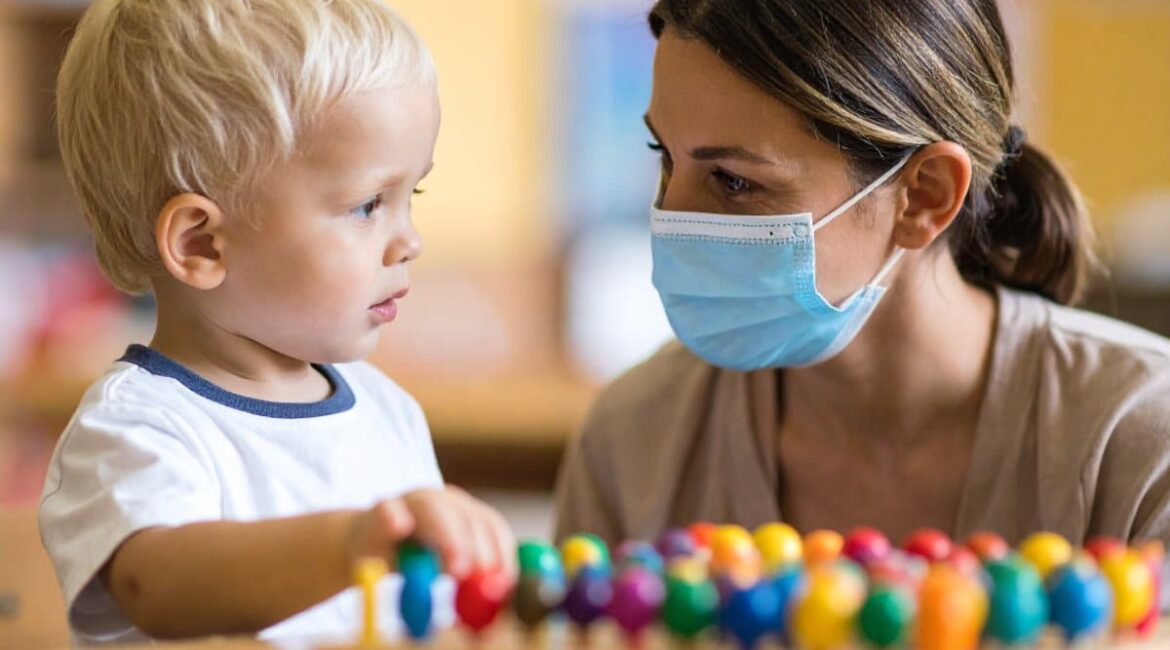
Toddlers Learn Without Seeing Tongues: Questions Don’t Muffle Word Learning
Summary: Toddlers as young as two can successfully learn new words even when a speaker’s mouth or eyes are covered, a study shows. Researchers found that children’s ability to follow the speaker’s gaze and link words to objects drives vocabulary learning, not reliance on seeing mouth movements.These findings ease concerns...