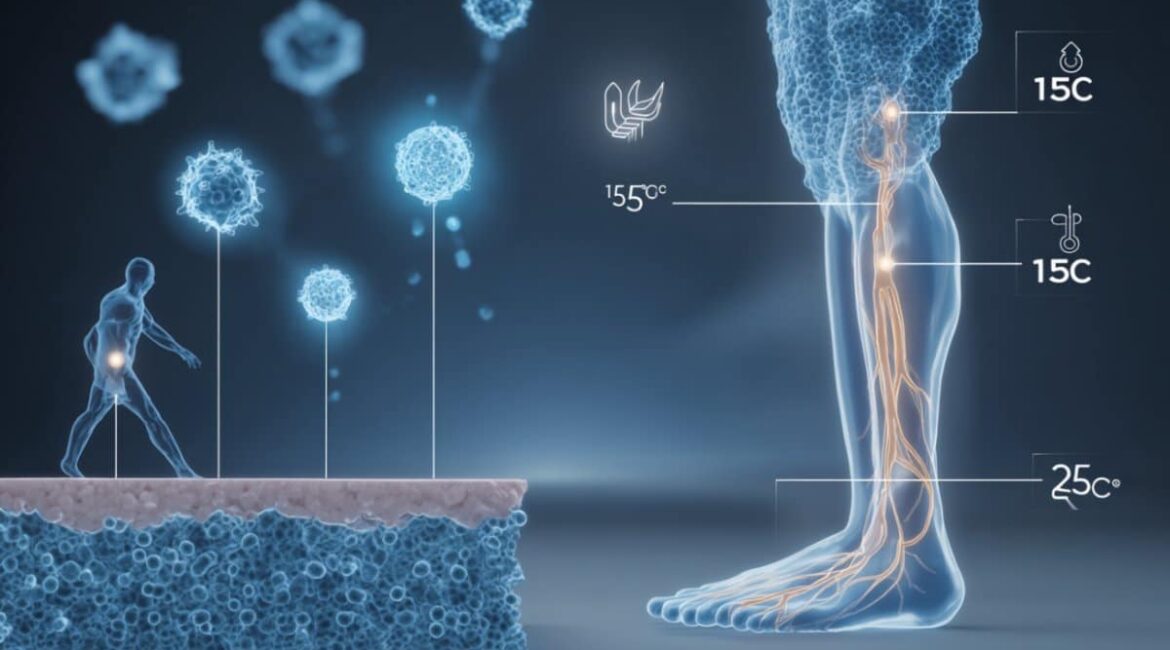
Key Questions AnsweredQ: What did researchers discover about how we sense cool temperatures?A: The study identified a complete neural pathway from the skin to the brain dedicated to detecting cool temperatures, showing how this sensation is transmitted and amplified in the spinal cord.Q: Why is this discovery important?A: It’s the...
How Much Pain You Experience Depending on What You Hope.
Key Questions AnsweredQ: How do expectations influence pain perception?A: Expectations shaped by external cues (like visual signals) and those shaped by treatment information (like placebo explanations) both reduce pain, but they do so in different ways and affect different brain systems.Q: What did brain imaging reveal about these effects?A: Only...
Women’s Ovulation Scent Alters Male Stress and Attraction
Key Questions AnsweredQ: What did the study find about female body odor during ovulation?A: Researchers identified three specific scent compounds that increase during ovulation and found they made armpit odor samples smell more pleasant to men, who also rated associated faces as more attractive and feminine.Q: Did these compounds affect...
Unregular Nap is Related to 172 Disorders
Key Questions AnsweredQ: What did this study reveal about sleep and health?A: An analysis of sleep data from over 88,000 people found that poor sleep patterns—especially irregular bedtimes and unstable circadian rhythms—were linked to elevated risk for 172 different diseases.Q: Which sleep traits were most harmful?A: Going to bed after...
Chronic Fatigue and Long COVID perhaps be attributed to your colon.
Key Questions AnsweredQ: What did the study uncover about ME/CFS?A: The study revealed that ME/CFS disrupts key interactions between the gut microbiome, immune system, and metabolism, identifying biological markers that distinguish patients from healthy individuals with up to 90% accuracy.Q: How does the AI platform, BioMapAI, help?A: BioMapAI integrates thousands...
How Astrocytes Maintain Neural Team Synchronization
Key Questions AnsweredQ: What did scientists discover about astrocytes and information encoding?A: The study found that astrocytes regulate ambient GABA levels using a protein called Gat3, which is essential for helping neurons coordinate their activity and encode visual information as a group.Q: What happened when Gat3 was removed from astrocytes?A:...
Trauma in childhood does rewire the brain to support ongoing aggression
Key Questions Answered:Q: What brain region is being studied to understand aggression?A: Researchers are focusing on the thalamic nucleus reuniens, which connects memory, emotion, and decision-making areas of the brain and may play a key role in impulsive aggression following trauma.Q: How does early-life trauma influence aggression later in life?A:...
How the Brain Recognition Emotional Experience
Key Questions Answered:Q: Why do emotional memories feel more vivid than neutral ones?A: Because emotional memory encoding involves unique coordination between the amygdala and hippocampus, which boosts recall strength.Q: What did the study reveal about brain activity during memory retrieval?A: Gamma activity patterns formed in the amygdala during emotional encoding...
Can Mental Illness Started Before You’re Born?
Key Questions Answered:Q: When do genes linked to mental illness start affecting the brain?A: Many genes associated with neuropsychiatric and neurodegenerative diseases are active during the earliest stages of fetal brain development—far earlier than previously believed.Q: How did researchers uncover this early genetic activity?A: By simulating the effects of nearly...
Exploration and Emotional Exploration to Discover Life’s Meaning
Key Questions Answered:Q: What is the “Geographic Model of Meaning in Life”?A: It’s a conceptual framework proposing that life’s meaning is not fixed but emerges as individuals explore their lives with different attitudes and emotional states—much like navigating a terrain by touch.Q: How is this model different from traditional philosophical...